口座開設は無料。オンラインで簡単にお申し込みいただけます。
最短3分で入力完了!
Sales Trader
サマリー: リスク・リバーサルは、コール・オプションとプット・オプションの両方を利用し、原資産を直接買うよりもダイナミックなペイオフを生み出すマルチレッグ・デリバティブ戦略です。最も基本的なリスク・リバーサル戦略のひとつは、アウト・オブ・ザ・マネーのプット・オプションを売り、同時にアウト・オブ・ザ・マネーのコール・オプションを買うというもので、これは通常、トレーダーや投資家が株式をショートしている場合に用いられます。この記事では、リスクリバーサル戦略を使って株式を積み立てることに焦点を当てます。
※本レポート内日本語は、ご参考情報として原文(英語)を機械翻訳したものです。
リスク・リバーサル戦略による株式ポートフォリオの構築
優秀な投資家は、株式を購入するために、人気のある現金担保プット戦略をよく利用する。しかし、この戦略の利用者は、株価がリトレースメントなしに上昇し、希望する価格で株式を購入する機会を逃してしまうというリスクに直面する可能性がある。このような場合、投資家は強気だった銘柄の上昇に参加できないことになる。
図解ペイオフ
例
Kc = アウト・オブ・ザ・マネー(OTM)コール・オプションの権利行使価格
Kp = アウト・オブ・ザ・マネー(OTM)プット・オプションの権利行使価格
このペイオフ・ダイアグラムでは、KpはOTMプット・オプションの売りの権利行使価格を、Kcはロング・コール・オプションの権利行使価格を表している。対称的なOTMプット・オプションとOTMコール・オプションのコストは、金利水準や市場センチメントなどさまざまな要因によって異なる可能性がある。
満期時に株価がKpとKcの間にある場合、ペイオフはプット・オプションの売りで受け取ったプレミアムとコール・オプションの買いで支払ったプレミアムの差額となる。株価がKcよりも上昇した場合、ペイオフはKcの価格からロングしたのと同じになり、正味のプレミアムを受け取ることになる。逆に、株価がKpを下回れば、ペイオフはKpからのロングと同様である。
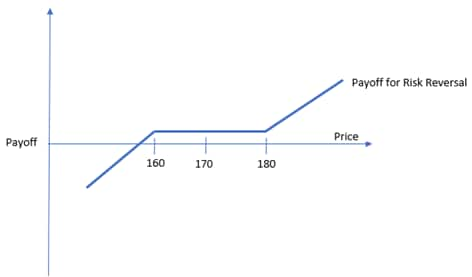
例
アップルが現在170ドルで取引されているとしよう。あるトレーダーがアップル株を160ドルで100株買いたい。このトレーダーは、アップルが160ドルを下回らずに上昇し続けることを懸念し、同時に権利行使価格180ドルのOTMコール・オプションを1.60ドルで購入した。コール・オプションのコスト($1.60)は、プット・オプションの売却で受 け取ったプレミアムで完全に相殺された。トレーダーは1株当たり1.40ドルの正味プレミアムを受け取った。
シナリオ1: アップルが160ドルを下回る
投資家は160ドルでアップル株を割り当てられる。損益分岐点=$160-$1.40=$158.60。
シナリオ2: アップルが180ドルを超える
投資家にはアップル株は割り当てられない。このトレーダーは権利行使価格180ドルのコール・オプションをロングしているため、このコール・オプションを行使してアップル株を180ドルで買うことができます。損益分岐点=$180-$1.40=$178.60。
シナリオ3: アップルが160ドルから180ドルの間で取引される
投資家は、アップル株を割り当てられることも、オプション行使によってアップル株を購入することもない。オプション戦略から受け取るプレミアム=1.40ドル/株
まとめ
リスク・リバーサルは投資家のツールキットとして有用な戦略である。特に、プット行使価格を下回ることなく株価が上昇し続 けた場合に、プット売りで株式を積み立てつつ、上昇の可能性を保持したいと考える株式投資家にとってはそうである。このアップサイドを保持したい投資家は、プット・オプションの売却代金の一部を使って、アウト・オブ・ザ・マネーのコール・オプションを購入することで可能です。しかし、株価が横ばいで推移すると確信している投資家は、現金担保プット戦略(プット・オプションの売りのみ)を利用することで、プレミアムを節約することができる。
Using the Risk Reversal Strategy to Build an Equity Portfolio
Good investors often use the popular cash secured puts strategy to buy stocks. However, the users of this strategy can face the risk that the stock rallies higher without any retracement, therefore missing out on the opportunity to buy the shares at their desired price. In such instances, these investors would not be able to participate on the upside of the stocks they were bullish on.
In order to avoid such a scenario, investors can look to buy an out of the money call option with the same expiration date using their premium gained from the sale of the put option. This combination of selling a cash secured put and buying a call option is called a Risk Reversal.
Risk Reversal = Sell an out of the money (OTM) put option + Buy an out of the money (OTM) call option with the same expiry date
Legend
Kc = Strike for out of the money (OTM) call option
Kp = Strike for out of the money (OTM) put option
In this pay-off diagram, Kp represents the strike for selling the OTM put option while Kc represents the strike for the long call option. The cost of a symmetrical OTM put option and OTM call option can differ depending on a variety of factors including the level of interest rates and market sentiment.
When the price of the stock remains between Kp and Kc at expiry, the payoff would be the difference between the premium received from selling the put option and the premium paid for buying the call option. If the price of the stock rises above Kc, then the pay-off would be similar to being long from the price of Kc + the net premium received if any. Conversely, if the stock falls below Kp, the pay-off would be similar to being long from Kp + the net premium received if any.
Let’s say Apple is trading at $170 now. A trader wishes to buy 100 Apple shares at the price of $160. Instead of placing a limit buy, he sells an OTM put option at strike 160 expiring in 1 month for a premium of $3. Concerned that Apple might rally continuously and not fall below the price of $160, he simultaneously bought an OTM call option at strike 180 for $1.60 with the same expiry date. The cost of the call option ($1.60) was completely offset by the premium received from the sale of the put option. The trader receives a net premium of $1.40 per share.
Scenario 1: Apple goes below $160
The investor would be assigned Apple shares at $160. Breakeven point = $160 – $1.40 = $158.60.
Scenario 2: Apple goes above $180
The investor would not be assigned any Apple shares. Since he is long a call option at strike 180, the trader is able to exercise this call option to buy Apple shares at $180. Breakeven point = $180 - $1.40 = $178.60.
Scenario 3: Apple trades between $160 and $180The investor would not be assigned any Apple shares nor will he be buying Apple shares through an option exercise. Premium received from option strategy = $1.40/share
Summary
The risk reversal is a useful strategy in an investor’s toolkit. This is especially so for stock investors who wish to accumulate shares by selling puts while still retaining upside potential if the stock rallies continuously without falling below the put strike. Investors who wish to retain this upside can do so by buying an out of the money call option using some proceeds from the put option sale. However, if investors feel confident that the stock will trade sideways, then they can save some premium by utilizing the cash secured puts strategy (only sell the put option).